Osteopathy
When injury prevents you doing what you love, it can be miserable. If you need an osteopath, you can be confid...
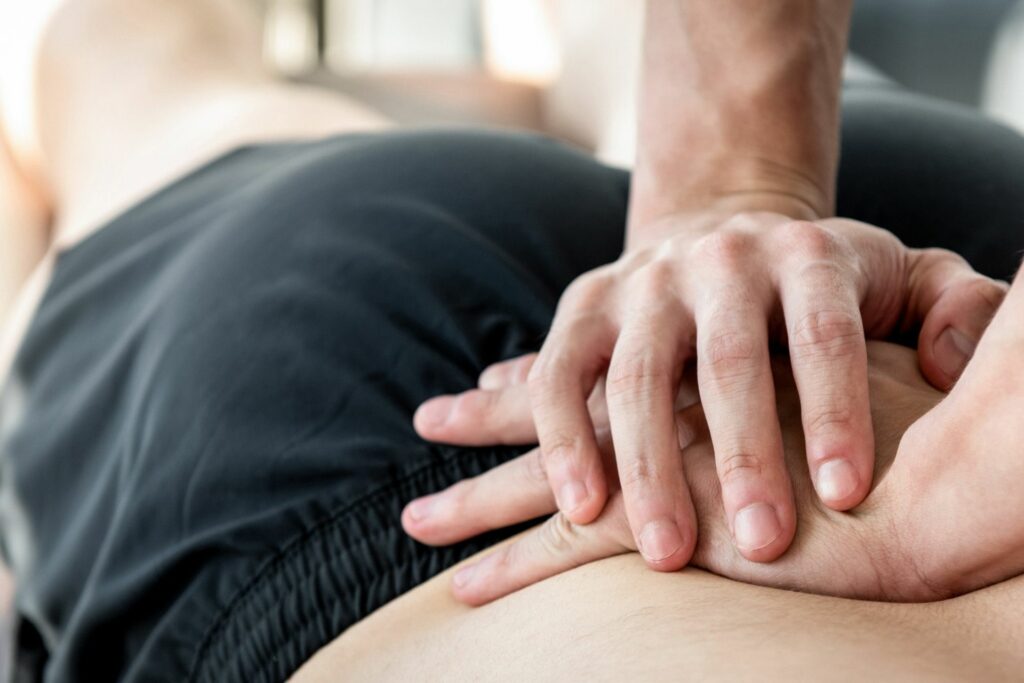

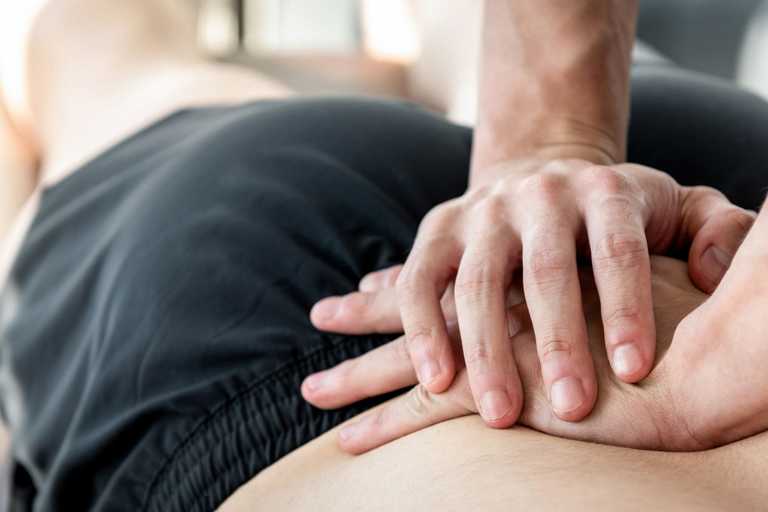
Both physiotherapy and osteopathy play vital roles in modern-day healthcare. While there is some overlap in treatment protocols and options between the two, they are distinct disciplines, often used in conjunction with a range of other medical approaches.
At Prime Health, we provide a full range of healthcare support for patients, including access to highly qualified and experienced physiotherapists and osteopaths and the imaging diagnostics they need which can make a huge difference to individual well-being.
Physiotherapists treat people who are affected by a wide range of health challenges and are seen in many clinical settings. An individual may have limited mobility and physiotherapy can help by improving their mobility and strength. After an injury following an accident or post-surgery, someone might need various therapeutic interventions to help them recover.
A physiotherapist will use a variety of approaches including manual therapy, massage as well as recovery through movement and exercise. They can also help individuals make positive lifestyle changes including advice and education to improve diet and flexibility.
Osteopathy, on the other hand, tends to focus on the function and structure of specific body areas like muscles, joints and bones as well as ligaments and connective tissues.
An osteopath will use a range of techniques involving manipulation to improve movement, boost blood flow and enhance the body’s own ability to recover. While it is more focused on the musculoskeletal structure and how its various elements work together, it uses a variety of holistic or whole-body techniques.
Both disciplines are complementary and offer minimally invasive approaches that use a range of natural healing mechanisms, from soft tissue treatment to improving general musculoskeletal health.
Whether you are referred to a physiotherapy clinic or an osteopath will depend on the nature of your health problem and how best it can be treated. In both cases, patients are directly involved in their own treatment and often play an active role.
Here we look in detail at the difference between osteopathy vs physiotherapy and which one might best suit your particular health issue.
Most major NHS medical clinics and hospitals will have trained physiotherapists on site. Some of these provide general physiotherapy services, others are more specialised. You’ll also find physiotherapy offered in private clinics, delivering a wide range of services including specialist sports injury and rehabilitation.
The role of the physiotherapist is to improve movement and body function through a range of non-surgical approaches such as manipulation, massage, heat treatment and exercise. It is considered a primary healthcare profession and plays a vital role in recovery from a wide range of conditions.
For example, if your hand has been injured in an accident and you need surgery, once you have recovered from surgery physiotherapists will take over the next stage of recovery by working on a range of movement and flexibility issues you may have through gentle physical manipulation.
A physiotherapist can become involved in your treatment if you have neurological, neuromuscular, cardiovascular or respiratory issues that need to be improved.
Here are just some reasons why you may be referred to a physiotherapist following your primary treatment.
A variety of different health problems have neurological effects – where the nerves are damaged or don’t function properly.
If you have a stroke, for example, you will almost certainly experience effects such as muscle weakness and loss of movement in some parts of the body. The role of the physiotherapist is to work with the individual to improve muscle control and regain strength. This can involve a long period of rehabilitation that can take months of carefully designed therapeutic interventions.
Physiotherapists are also involved in helping patients cope with complex neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple Sclerosis, generally working in partnership with other treatments and healthcare professionals to deliver beneficial results. That can include methods to relieve pain and improve blood and nerve supply.
In the UK alone, around 8 million people are currently living with some form of heart and circulatory disease, and there are 160,000 deaths each year. Physiotherapy plays an integral part of the recovery process for cardiovascular disease and can have a profound effect on health and well-being as well as life expectancy.
Approaches include helping patients to recover from initial critical events as well as developing specialist exercise and nutrition programs to improve cardiovascular health in the longer term.
This can vary from more common issues such as asthma to highly complicated health conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
For example, a physiotherapy team can help those with serious asthma to retrain their breathing and introduce exercises to aid them in coping with attacks.
In particular, physiotherapy treatment has been shown to be highly effective in helping patients cope with COPD, improving their life chances and general health and well-being.
Not all health issues that physiotherapists can help with are life-threatening. Many people in modern society suffer from problems such as chronic back and joint pain.
There are others who might have had an accident that caused a fracture or a broken bone that requires further assistance once the injury has healed sufficiently. In addition, physiotherapists often help to treat sports injuries such as muscle damage or joint and tendon problems.
If you have an issue such as joint pain or a chronic low back problem, for example, a physiotherapist will work with you by employing approaches such as spinal and joint manipulation and helping to reduce musculoskeletal pain.
Physiotherapy assessments can vary depending on your health problem and the prior involvement of other healthcare services. One of the most common issues physiotherapists deal with is lower back and neck pain.
A physiotherapist will start by looking at your medical history, lifestyle and any treatment that you are currently undertaking.
Diagnostic imaging tools such as MRI scans, ultrasound, CT scans and x-rays are particularly useful in providing a clear picture of internal conditions for low back pain and can help determine the type of treatment and care that should be given, both in the short and long term.
How long treatment takes obviously depends on the nature of the problem and the extent of any injury or mobility issue. Physiotherapy can take several months or many years because of this. Obviously, the time it takes to recover from a sports injury such as a torn hamstring will be different to the rehabilitation you need following a serious car accident.
A physiotherapy team will draw on a wide range of treatments and approaches including:
Do you need an appointment for a physiotherapist? Book an appointment today – click here.

While physiotherapy has more wide-ranging applications in modern healthcare, osteopathy tends to focus on the diagnosis and treatment of musculoskeletal problems.
One of the key philosophies is that parts of the body are interrelated and treatment needs a holistic approach.
The main focus of osteopathy is the bones, joints, ligaments and connective tissues and it is concerned with body systems as a whole. It can be used for both maintaining good health (for example, addressing poor posture issues) and for addressing various physical issues such as low back pain. Physiotherapy, on the other hand, is concerned with rehabilitation, usually following injuries or other medical problems.
A large part of osteopathic treatment is the manipulation of the joints and body. Joint manipulation can often cause a ‘cracking’ sound and other approaches such as massage and stretching are also employed.
You will visit an osteopath if you have musculoskeletal problems. These may include:
Whereas people usually only see physiotherapy when they have a specific health problem such as an injury, osteopaths also provide support for maintaining good health, like helping to reduce bad posture issues such as rounded shoulders which can eventually lead to chronic neck pain.
Some osteopaths also specialise in areas such as sports, not just helping individuals to recover from injuries but also offering services that prevent them from occurring in the first place and even improving their athletic performance.
As with physiotherapists, an osteopath will start any treatment by taking a full clinical history to get a complete understanding of what your health issue is.
An osteopath will tend to have a more holistic approach when examining you – for example, if you have neck pain, they may also look at other parts of the body such as the pelvis and lower limbs which could play a role in your condition.
In many clinics, such as Prime Health, an osteopath will have access to high-quality diagnostic imaging tools such as CT and MRI scans, ultrasound and x-ray.
Osteopathy treatment times can vary considerably depending on the condition that you are having treatment for. Sessions typically last for around 30 minutes after the initial consultation and you may need to attend regular appointments over several months to see the true benefits.
Do you need an appointment for an osteopath? Book an appointment today – click here.

It’s important that you get a full and accurate diagnosis if you have a health issue requiring input from an osteopath or physiotherapist. Physiotherapists tend to be more focused on rehabilitation for a wide range of conditions and osteopaths tend to take a holistic approach to musculoskeletal health problems such as chronic back and joint pain.
At Prime Health, we offer a full range of medical services that are designed to get to the root of your problem. With access to state-of-the-art diagnostic imaging services including MRI and CT scans, x-ray and ultrasound, we can ensure that our team of highly experienced osteopaths and physiotherapists are able to give you the support that you need.
While osteopaths and physiotherapists can often perform similar roles in modern healthcare, they are different disciplines. Osteopaths are largely concerned with musculoskeletal well-being while physiotherapists are focused on rehabilitation for a much wider range of conditions.
Prime Health combines the latest diagnostic imaging technology and services with highly qualified healthcare teams. You can find out more here.
Do you need an appointment for an osteopath or physiotherapist? Book an appointment today – click here.
When injury prevents you doing what you love, it can be miserable. If you need an osteopath, you can be confid...
The physiotherapists that work at Prime Health are among the most effective and experienced in the country - m...
The highly experienced private GPs at Prime Health are here to keep you healthy. In a fast-moving world, they ...
Prime Health gives you fast access to the latest MRI expertise and 3T technology so you can get diagnosed and ...
If you don’t have a referral from a health professional, you can now easily self-refer for an MRI scan at Prime Health. We offer daily appointments, allowing you to choose a time and date that suits your convenience.